
The existence of 3D-printers is not the news today. The current models are able to print a variety of plastic products, food, chocolate, shoes and even accessories. The main feature is that 3D-printers print human organs from biological material. Such an invention would be a revolutionary breakthrough, because donor agencies are the large deficit today. They need hundreds of thousands of patients around the world who are waiting in long queues for transplantation, and only the tens of thousands become the owners of the donor organ. 3D-printers changed the face of transplantation medicine, so this issue should be considered.
Every year hundreds of thousands of people die due to lack of organs for transplantation, that means that artificial organs can save these lives. And now scientists have made a major breakthrough, having established “bioprint” of artificial vascular networks. According to a study, researchers at the University of Sydney, MIT, Harvard and Stanford successfully printed blood vessels, offering 3D-printed authorities access to nutrients and oxygen, as well as the opportunity for recycling (Roebuck, K., 2011).

Besides practicing the idea of its creation belongs to the scientists from the Institute for Regenerative Medicine, Wake Forest, who began to use 3D-printer for synthetic building blocks for growing human bladders. In fact they did not print bladders, and the first printing of this body appeared only in the early 2000s. At this time, a bioengineer at the University of Clemson Thomas Boland began to modernize conventional ink-jet printers to give them the ability to print three-dimensional objects from the biological material. By 2010, the Organovo became well-known company in this field. The company is currently engaged in printing samples of human liver. However, these organs are not yet fully functional, they cannot be used for transplantation.
To understand the purpose of 3D printing we should consider its internal process and to look at the picture of the printer. For 3D-printing scientists use advanced bioprinter and scientists produce thin interconnected fibers. They were covered with human endothelial cells (the inner walls of the blood vessels) and applied on the protein material. After strengthening the entire structure of the light, they carefully removed the fibers, leaving a complex network of cellular material. A week later, the cells were organized in stable capillaries. The cells inside the printed vascular networks survived, differentiated and proliferated faster than cells that did not receive the nutrients (CSC LEADING EDGE FORUM, 2012).
We can define several key challenges of creating artificial organs by using 3D-printing. The first problem is the shortage of material from which it is possible to produce human organs. In addition, it is extremely difficult to make the right cells to grow outside the body. Human bodies are arranged very difficultly, therefore, it is not easy to establish a working artificial organ, despite the fact that it is natural and consists of the same cells. You cannot just make printed body and hope that everything will be okay. Even if the cells are divided into artificial organs outside the body, it does not mean that they will work smoothly. In addition, the scientist notes that there are still limited technical possibilities: yet so powerful equipment, that would create a model of that best meet real. In addition, it is difficult to make the cells involved in the coordinated work, scientists have to solve one complex problem of production of blood vessels. Arteries, veins and capillaries just need to make all the organs to function correctly, because with their help, a variety of fabrics are delivered to the nutrients in the blood, that allow to save the lives and health authorities. Dist blood vessels are very difficult due to their particular shape, length and width (Michael Weinberg, 2010).
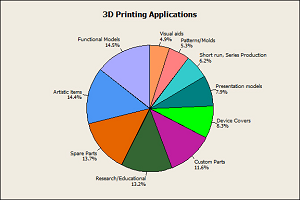
In addition to organ transplantation, 3D printing may be used in various fields of medicine in future. This will help not only to make the donation of organs, but also to ensure better healing and recovery of patients, and the best medical education for working professionals and students. Some practical examples where people can use these technologies are connected with the ethical principles, that confirm the useful nature of 3D printing:
Government. The most obvious use of 3D printing bodies transplants. It is impossible to overestimate the ability to create new organs directly from the patient’s own cells. It could save tens of thousands of lives each year.
Support of skeleton. Fabrication of complex and detailed objects is one of the strengths of 3D printing, so the 3D-printer is already used in order to create biodegradable structures to support the skeleton, to help and facilitate the healing of the patient and tissue growth.
Replacing the bones. In conjunction with 3D- scanning, 3D-printers can create a bone, such as the femoral, that is ideal for those who need a new bone.
Practice Operations. When a person visits a doctor, he wants to know that he is in good hands. With 3D printed organs future surgeons could perform tens or even hundreds of operations before doing the same operation to a real person. The opportunity to get the best surgeons practice means that the operation as a result of need less time, and recovery will be faster.
Testing medicines. No one likes the idea of drug testing, whether in animals or in humans. But then again, we all want to know that our medicines are tested and safe. With 3D printing we will forget about the testing of drugs on humans and animals. It will also contribute to the continuous development of medicine (Vladimir Mironov, Thomas Boland, Thomas Trusk, Gabor Forgacs and Roger R. Markwald, 2013).
So in the nearest future the person will get a new body only by clicking “Print” on the computer screen. Here are analyzed key researches to achieving this goal. Scientists have made some progress in growing blood vessels in the lab, creating a vein of the donor cells of blood vessels and putting them on the tube biodegradable timber. But 3D-printing technology can make the process much more real, increase the speed and reduce the costs. In conclusion, the new technologies can save someone’s life, and this is a good deal.
References:
Roebuck, K. (2011). 3d printing. S.l.: Emereo Pty.
Vladimir Mironov, Thomas Boland, Thomas Trusk, Gabor Forgacs and Roger R. Markwald (2013). Organ printing: computer-aided jet-based 3D tissue engineering
Michael Weinberg (2010). 3D Printing, Intellectual Property, and the Fight Over the Next Great Disruptive Technology.
[https://www.publicknowledge.org/files/docs/3DPrintingPaperPublicKnowledge.pdf]
CSC LEADING EDGE FORUM (2012). 3D printing and the future of manufacturing.
[http://assets1.csc.com/innovation/downloads/LEF_20123DPrinting.pdf]
|
Grammar
C
|
Formatting
B-
|
Organization
B
|
Style
C+
|
